FAQ

FAQ: Frequently asked questions
1. What is a stepping motor drive?
The stepping motor controller produces the step sequence for the stepping motor. Depending on the motor and on the operation mode there are e.g. sequences of 4 steps (full step) up to 128 mini-steps (1/32-step). After the last step of a sequence was done, it starts once again from the beginning. The controller manages the temporal succession of the steps. E.g. it makes available: A starting frequency, an acceleration curve, a driving frequency, a brake curve and a stop frequency. Higher speeds can only be achieved by a defined pull-out curve. It can be left by a selected brake ramp only. The controller determines the spatial and temporally course of the movement. By counting the number of steps the controller is able to persue the current position.
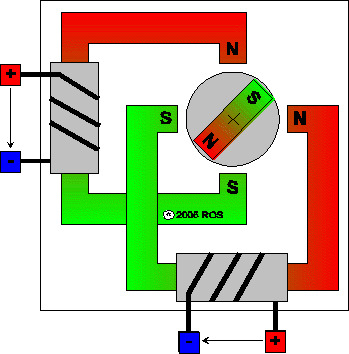
Step 1
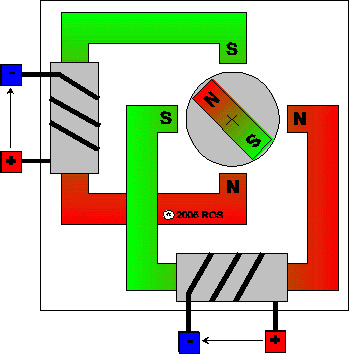
Step 2
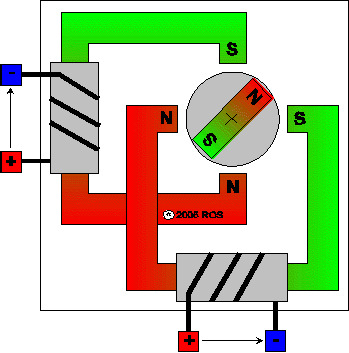
Step 3
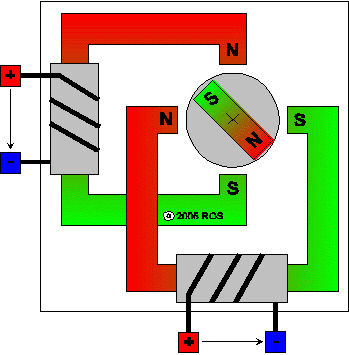
Step 4
2. What is a stepping motor drive for?
3. What are the benefits of a stepping motor drive?
The durable stepping motor drive can be used under adverse environmental conditions: e.g. ideally suitable for high operating temperatures, vibrations, shocks and so on.
There is no restriction of the angle of rotation. In STOP-position a retaining moment is possible. If necessary a retaining torque up to the nominal torque is possible.
The only substantional wearing parts which are worth to be mentioned are the bearings of the motor.
4. What are the disadvantages of a stepping motor drive?
Resonant frequencies, which can occur particularly in the full step operation, cause noise and step-losses may occure. The solution are purposeful measures in the mechanics (e.g. reinforcement, absorption) and/or the choice of another motor and/or the choice of another resolution (half step, mini step).
5. What kinds of stepping motors are available?
The hybrid motors have finer structures and are more complex in construction and manufacturing. In this case ball-bearings are used. Typical step angles are 1.8 degrees for the 2-phase motor and 0.72 degrees for the 5-phase motor.
The benefit of the disk magnet stepping motor is (among other things) a very small rotor moment of inertia. Therefore it is inserted in high-dynamic drives very often. Some motors have very good micro stepping characteristics. Typical step angles are 3.6 degrees and 1.8 degrees.
The windings of the 2-phase motor in many cases are alternatively available in unipolar (6 connections, for each coil beginning, center, end) or bipolar (4 connections, for each coil beginning and end). In the bipolar mode the full copper volume is always used. In the unipolar mode only half of the capacity is used. Some motors are available with 4 coils (8 connections), which can be switched in row or parallel .
6. What are the differences between the controllers?
On the other hand there are important differences in electrical handling of the motor coils: The simple constant voltage mode needs only few elements. However, thereby the motors do not achieve their full performance. The constant current mode is more complex in the construction, but it improves the motor performance very much and micro stepping becomes possible.
7. What is a reference drive for?
After switching the device on, a reference drive is normally made first. It ends with the finding of the point of reference. This point is defined in the simpliest case by a mechanical barrier but better by an electrical contact.
